Concept of Electrical and Electronics: The branch of engineering or technology that deals with the flow of electrons through conductors is called electrical. On the other hand, the branch of technology that deals with the flow of electrons through vacuum or semiconductor devices is called electronics. The difference between the two is that in the case of electrical, electrons flow through conductors and in the case of electronics, electrons flow through vacuum or semiconductors.

Concept of Electricity: Electricity is an invisible energy that can be converted from one energy to another. With its help many practical tasks are completed by generating light, heat, sound, motion etc.

Use of electricity: We use electricity to run lamps and fans, watch television, charge mobile phones, run motors to pump water into rooftop tanks or irrigate fields, run laptops or computers, use electricity to operate cameras or microphones and speakers.
List of Electrical and Electronics Equipment:
| Electrical Equipment: | Electronics equipment: |
| 1. Electric lamp 2. Electric fans 3. Electric motor 4. Electric oven 5. Generator 6. IPS/UPS 7. Voltage stabilizer 8. Fridge 9. Transformer 10. Switch gear 11. Magnetic contactor 12. Circuit breaker | 1. Television 2. Mobile phone 3. Desktop computer 4. The camera 5. Photocopier 6. Scanner 7. Printer 8. Laptop 9. Multimedia projector 10. Telephone 11. Radar 12. Amplifier |
Definition of Current, Voltage and Resistance:
Voltage: The pressure or force applied to make free electrons in a conductor flow in a particular direction is called voltage. The unit of voltage is volt. The instrument that measures this voltage is called a voltmeter.
Current: The rate of flow of electrons or charge through a conductor is called current. The unit of current measurement is ampere. The device with the help of which this current is measured is called ammeter.
Resistance: The characteristic or behavior of a conductor that hinders the flow of current through it is called resistance. The unit of resistance is ohm. The instrument used to measure this resistance is called an ohmmeter.
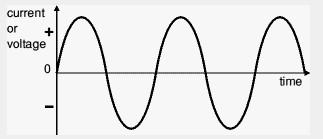
Alternating Current or AC:- The current which changes in value and direction with time is called Alternating Current or AC.
DC or Direct Current: A current whose value and direction remain constant over time is called direct current or DC.
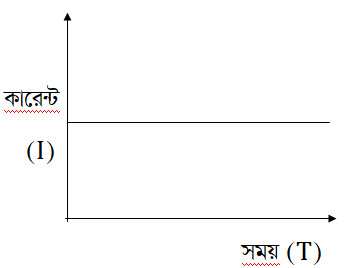
Basic difference between AC and DC:- The basic difference between AC and DC is that AC current is variable and DC current is constant or constant.
Types of Personal Protective Clothing (PPE):

1. Skin Protector: Apron, worn to protect body and clothing from dirt and to identify individuals.
2. Hand and arm protectors: Gloves, which protect the body from body charges and the hands from sharp parts of the equipment.
3. Head Protector: Helmet, it protects the head.
4. Foot protectors: Safety boots, which protect against electric shock, are used for climbing electric poles.
5. Eye Protection or Safety Goggles: Safety goggles are used as eye protection to prevent any splashes from falling into the eyes during manual work.
Requirement of Personal Protective Clothing (PPE): In real life, people working in hospitals, science labs/laboratories, electrical lines etc. use a garment that covers most of the entire body that is PPE. PPE is a very important part of ensuring your safety at work. Without PPE, accidents are often encountered in the workplace. It can even lead to human death. So it is important to use PPE in electrical work like in other work areas.
Electrical Accessories: In ICT and IoT workplace we need to use some necessary electrical accessories or parts. Eg-Switch: This switch is used to switch the power on or off the electrical power line. There are also more- sockets, multiplugs. Essential electrical accessories like power cables, circuit breakers, fuses, cutouts, relays etc.

Electrical Components:
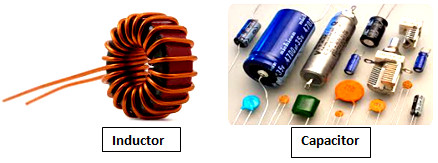
Capacitor: If two conductive materials i.e. conductors are separated from each other by an insulator, then its charge capacity increases due to AC flowing through it. Such a charge holder is called a capacitor. The characteristic of the capacitor is that the higher the frequency of the current flowing through it, the lower the resistance to the current flow.
Inductor: It is a type of passive two-terminal electrical components or parts. AC current flowing through the coil of wire creates resistance. The characteristics of the inductor are – If the frequency of the current flowing through it increases, the value of the resistance increases, on the other hand, if the value of the frequency decreases, the value of the resistance decreases.
Semiconductor devices used in ICT workplace:
Semiconductor devices widely used in the ICT workplace are various types of components including rectifier diodes, Zener diodes, LEDs, transistors, regulators, operational amplifiers and ICs.
Diode: Diode is a two-terminal p-n junction device. Diodes are used to convert AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage in power supply circuits.
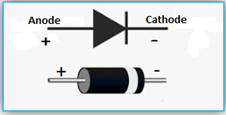
Zener Diode: This type of diode is used for voltage stabilization or regulation.

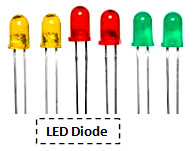
LED: Its full name is Light Emitting Diode. When current flows through this diode, light is produced.
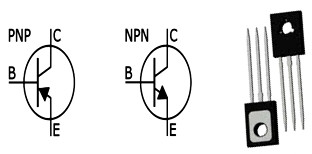
Transistors: Transistors are generally used for high speed switching and voltage amplification. It is a three terminal device. The terminals or ends are the base, emitter and collector respectively. Based on the current flow through the transistor it is divided into two categories namely:
1. NPN 2. PNP
Integrated Circuit (IC): An integrated circuit (IC) is basically a device composed of many semiconductor devices. In today’s electronics systems, many ICs and microprocessors can be integrated into a single integrated circuit to perform hundreds of circuits.
Measuring instrument:
At work we need to measure voltage, current and resistance and continuity test of circuit connections or parts, components and devices. The instruments that are used to perform these tasks are called electrical measuring instruments. These measuring instruments are of immense importance in electrical and electronics systems.
Function of Ammeter or Multimeter:- Function of multimeter is to measure current, voltage, resistance, frequency and continuity.
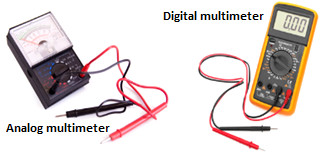
Analog multimeters are generally of two types namely:-
1. Analog multimeter
2. Digital multimeter
Following are the differences between analog and digital multimeters:
| Analog Multimeter | Digital Multimeter |
| 1. Analog multimeters display readings using an indicator running with a galvanometer. | 1. Digital multimeters display readings in digital numbers. |
| 2. The process of determining the value of the measured quantity in an analog multimeter is a bit complicated | 2. The valuation method is very simple |
| 3. An analog multimeter has a high margin of error | 3. The amount of error is low |
| 4. Data is less accurate | 4. Data is accurate |
| 5. function less | 5. function is more |
| 6. Cheap in price | 6. Over priced |
| 7. Less usage | 7. Use more |
ESD Device Concept: When an electrically charged device comes into contact with the human body, static electricity or charge from the human body or organ may enter the device. If this charge enters electronics devices, especially ICs and microprocessors, it can be damaged. The protecting device used while working with these circuits so that the charge generated by the human body cannot affect or damage the electronic devices is called electrostatic discharge or ESD device.

