
Electricity is a type of invisible energy that can be converted from one energy to another. With its help many practical tasks are completed by generating light, heat, sound, motion etc.
History of Electricity: Electricity is derived from the Greek word electron. The word electron means amber. In 600 BC, the Greek philosopher Thales noticed that rubbing amber with a silk cloth produced an invisible force and that the amber attracted small pieces of paper. Similarly, we see that when we run a hair through a comb and bring the comb near a small piece of paper, it attracts the pieces of paper. Basically, the effect of this invisible force is called electricity.
Classification of Electricity:-
Electricity is of two types namely:- 1. Static electricity
2. Running electricity
Static electricity
The electricity produced by friction is called the electric current. This electricity stays at the place where it is generated and does not leave the place where it was generated. So this type of electricity is called static electricity.
There are two types of charges in static electricity, one is positive charge (+) and the other is negative charge (-).
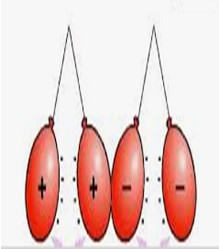
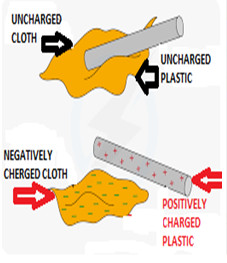
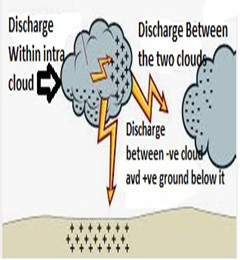
Above diagrams are examples of static electricity. In Figure 1, two positively charged balloons repel each other, but attract the oppositely charged balloon. In Figure 2, there is no charge between the piece of cloth and the plastic rod in the 1st state, but whenever the piece of cloth rubs against the plastic rod, the piece of cloth gets a negative charge and the plastic rod gets a positive charge. Figure 3 shows how the frictional electricity from the clouds descends to the ground.
Running current:-
Electricity that flows from one place to another without remaining stationary at the place of origin is called current electricity.
There are two types of electricity namely:-
1. direct current (DC
2. Alternating current (AC)
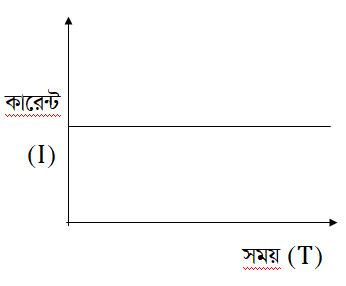
Direct current (DC)
A current which does not change in value and direction with time is called unidirectional or DC current.
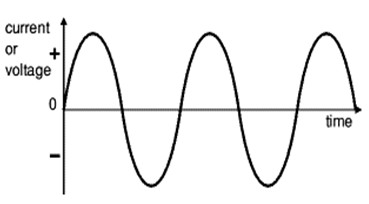
Alternating current (AC)
A current that changes in value and direction with time is called alternating current or AC current.
Effect of Electricity:
How many signs or results appear as a result of the flow of electricity through a circuit is called the effect or reaction of electricity.
Various effects of electricity are discussed below:-
1. Thermal Effect:– When electricity flows through a conductor, the conductor heats up and the electricity dissipates. In this case electrical energy is converted into heat energy so it is the thermal product of electricity. For example, Light scattering from electric lamps, heat radiation from heaters, etc. are thermal effects of electricity.



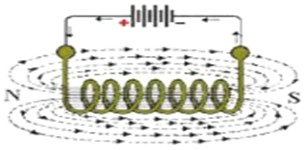
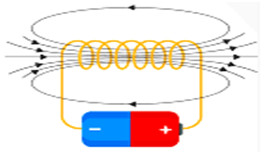
2. Magnetic Effect: When current flows through a conductor, a magnetic field is created around the conductor, converting electrical energy into magnetic energy. Electric clocks, generators, motors, etc. are operated by exploiting the magnetic effect of electricity.
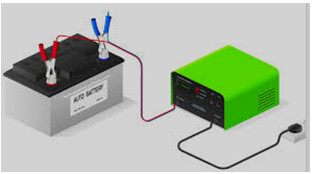
3.Chemical effect:- If electricity is passed through a solution of a compound, then the solution decomposes. When electricity is passed through acidic water, the water dissociates into hydrogen and oxygen. That is, electrical energy is converted into chemical energy.

4.Effect on living body:- If electricity flows in the living body, a kind of pain is felt, even the death of the living being can happen in the blink of an eye.
