A transformer is an electrical device that can be transferred from one coil to another coil by induction method without changing the value of power and frequency between the coils without any electrical connection.
Classification of transformer:-
There are two types of transformers based on the number of phases.
For example:- 1. Single phase transformer 2. Three phase transformers

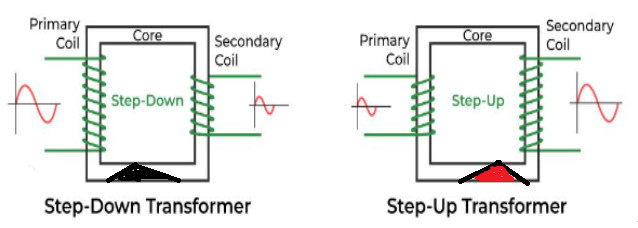
Again according to the process of transformers two types namely:-
1. Step-up transformer. 2. Step-down transformer.
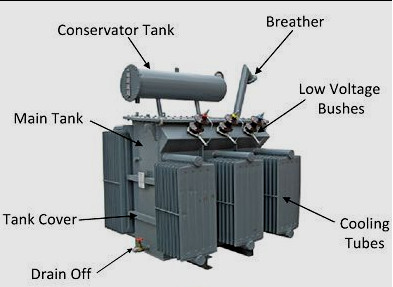
Constructional Details of a Transformer:
A transformer consists of the following parts:-
1. Main tank, 2. Core 3. High voltage winding 4. Low voltage winding 5. Radiator 6. Drain cork 7. Rollers 8. High voltage bushing 9. Low voltage bushing10. Conservator 11. Vent pipe 12. Transformer oil 13. Buchrez relay 14. Thermometer 15. Breather 16. Earthing terminal 17. Tap changer 18. Well level indicator 19. Lifting hook 20. Nameplate.
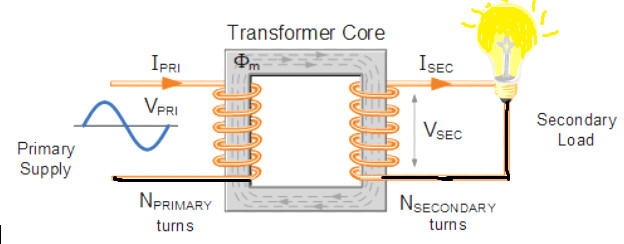
The Working Principal of Transformer
Voltage Generation in Secondary Coil of Transformer:-
We know that a transformer has two coils, one is primary coil and the other is secondary coil. Now with AC supply to the primary coil AC current flows through it. As a result, a variable flux is produced in the primary coil, which induces a voltage in the secondary coil of the transformer according to Farad’s principle of electro-magnetic induction. This generated voltage is called transformer voltage. The process by which this voltage is generated is called transformer action. This is how a transformer works.
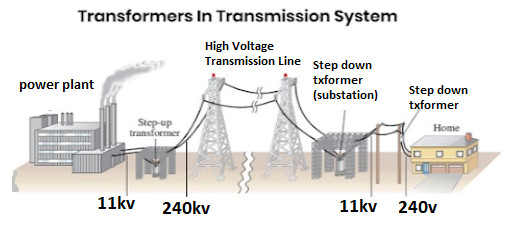
Use of Transformer:
Nowadays the role of transformer is very important in electrical work. Its practical aspects are discussed below:-
1. Transformers are used to convert low voltage to high voltage as required in transmission of electrical power over long distances.
2.Transformers are used to convert the higher voltage of the transmission line to lower voltage as required.
3. With the help of transformer in the distribution line, the voltage can be reduced to the required value of the consumers.
4. Transformers are used in various machinery and necessary testing of electrical, electronics and computer engineering.
5. Transformers are used in electrical communication circuits.
6. Transformers are used in radios, televisions, tape recorders, etc.
7. Instrument transformers are used for various measuring devices and protection devices used in electrical circuits.